





Just another Open Source Studio site





Concept
Sketch Model

We used straws to represents the mole rat’s tunnel. However the globules we made could not flow through due to the joining. We felt that it will be interesting if the audience gets to see movement of the globules. Hence, we replaced it with a transparent air tube and made the globules colourful.
Making of Final Model

We added a lot of globules, we thought that by doing so, we could reduce the amount of time for it to travel through the air tubes. However, we realised that it will cause a jam. It takes a long time before it exits.
We remove all the globules and tried putting in 5-8 globules. It only takes 6 pumps for the globules to exit the 5metres air tubes. It was much faster than what we expected.
How we show movement of animals


The Simethyltryptamine Slug produce a special chemical, (globules), The Hominid Frog(plastic cup) will follow the slug to absorb these molecules. These molecules will land on the Hominid Frog. When the frog releases its feces, the Pygmy Mole-Rats (toy car) uses the frog’s feces to line the entrance of their burrows.
Final Model






Relationship between The Hominid Frog, The Pygmy Mole Rat and the Simethyltryptamine Slug

The delicate relationship between these remarkable creatures takes place only in the Brazilian rain-forests.
Slugs feed on one particular fungus that only grows near one particular type of Cecropia plant, given the presence of pygmy mole-rats. This fungus allow the slug to produce a special chemical called the Simethyltryptamine or SMT.
The Hominid Frog will then follow the slugs to seek out the SMT. The slug secretes the SMT molecules through its skin which contained mucous. The frog will place its hands on the slug and absorb the molecules through special receptors in its finger tips. The Hominid Frog is the only species of animal with receptors in its brain able to bond with the SMT molecule.
Mole-rats will attach themselves to Hominid Frogs. As the Frogs seek out the SMT Slugs, so too do they encounter female Mole rats, essential to the irrigation and propagation of the SMT Slugs nutrients.
Once a pygmy mole-rat has found a mate, they will pair for life and dig burrows around the roots of the Cecropia plants.
Offspring do not stay near their birth plant, and leave to find other colonies to widen the gene pool. They will either venture by themselves or attach directly to another Hominid frog.
The pygmy mole-rats will also use the Hominid Frog’s feces to line the entrance of their burrows. This in-turn keeps predators away from their burrows, as the Hominid frog is deadly poisonous. The Pygmy mole-rat is the only animal equipped to resist the poisons of the frog.

Colony Behavior
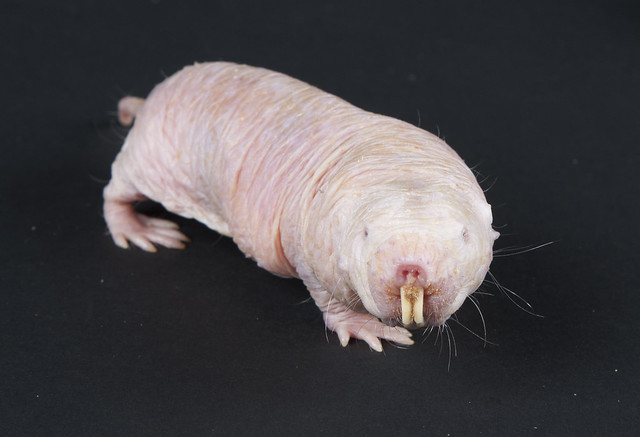
Naked mole rats are rodents, but they live in communities like those of many insects. Several dozen rats live together in colonies led by one dominant rat—the queen. As in some insect species, the queen is the only naked mole rat female to breed and bear young.
Worker animals dig the burrows that the whole clan inhabits, using their prominent teeth and snouts. They also gather the roots and bulbs for the colony to eat. Other rats tend to the queen.
Most other types of mole rats live on their own or in small families. Though mole rats spend most of their time excavating and foraging in their burrows, they occasionally emerge to search for seeds or other plants.
One interesting fact is the mole rats cuddle each other to sleep, to keep themselves warm.
Movement
The legs of a Pygmy mole rat is thin and short. However, they are highly adept at moving underground and can move backward as fast as they can move forward.
Their large, protruding teeth are used to dig and their lips are sealed just behind the teeth, preventing soil from filling their mouths while digging. About a quarter of their musculature is used in the closing of their jaws while they dig.
Senses
A pygmy mole rat is almost blind, they live underground, in the dark. Therefore the main senses it uses is hearing, sight and smell.
Who is Kokopelli?

Kokopelli is a fertility deity. Like most fertility deities, he presides over both childbirth and agriculture. He is usually depicted as a humpbacked flute player. Kokopelli’s flute is said to be heard in the spring’s breeze, while bringing warmth. It is also said that he was the source of human conception. Legend has it, everyone in the village would sing and dance throughout the night when they heard Kokopelli play his flute. The next morning, every maiden in the village would be with a child!
How do we hear?

The ear consists of three basic parts – the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Each part of the ear serves a specific purpose in the task of detecting and interpreting sound. The outer ear serves to collect and channel sound to the middle ear. The middle ear serves to transform the energy of a sound wave into the internal vibrations of the bone structure of the middle ear and ultimately transform these vibrations into a compressional wave in the inner ear. The human eardrum is a stretched membrane, like the skin of a drum. When the sound waves hit your eardrum, it vibrates and the brain interprets these vibrations as sound.

As shown above, a compression forces the eardrum inward and a rarefaction forces the eardrum outward, thus vibrating the eardrum at the same frequency of the sound wave.
Similarities between Humans and Frog hearing

A frog’s ear drum is called a Tympanum and works in very much the same way that our human ear drums work. A frog’s ear drum, just like a humans ear drum, is a membrane that is stretched across a ring of cartilage like a snare drum that vibrates.
There is rod that is connected to the ear drum, which vibrates by sounds that come at the frog. That sound is just pressure waves. Sound is localized by the time difference when the sound reaches each ear. The rod sloshes around in the inner ear fluid, which causes microscopic hairs to move, which send signals to the frog’s brain for interception. A frog’s ear lungs also vibrate when sound waves come toward it, although they are less sensitive than the frogs ear drum. Frogs also cannot hear short and high frequency sounds.
Body Parts

Function of the Spine
The spine has many functions, the main ones are listed below
In the assignment, we are supposed to create a fashion wear for Kokopelli. We had to incorporate sound into the body part we got! The body part that I got was spine.
Our spine serves a number of purposes. It is made up of 24 moveable bones that helps to support our weight as well as to hold us upright. Spine plays an important role in our movement.
The spine is connected from the neck all the way to the tail bone. It is composed by 3 different segments: the cervical spine, which it connected to the neck; the thoracic spine, which encompasses the shoulder and chest area; the lumbar spine, as know as the lower back; the sacrum; and finally the tail bone.
The facet joints of the spine allow back motion. Each vertebra has four facet joints, one pair that connects to the vertebra above (superior facets) and one pair that connects to the vertebra.

Every movement, every step, like picking up a pencil or dancing and even walking. It all requires the spine. As seen in the image above, our spine is very flexible, we can bend and twist easily. The spine is formed with many bones, each with a soft ‘disc’ in between. The purpose is for flexibility and reduction of stress on bones.
Sound
Pleasant Sound – Wind + Leaves
Smooth, Calming, Constant

Unpleasant sound – Echo
Sharp, Painful, Echos, Sudden

For this assignment, we are suppose to manipulate a basic 3D volume with the three words we got. The key words I got was Extrude, Skew and Pack.
Pack: very close together / a few items Extrude: being forced out Skew: slanted / distorted in a way
Module 1:


For my first module, I define pack as a group if cubes being stick together ( a pack of 4) And I combine extrude and skew into a single object.
Module 2:


The second module, I started skewing the entire model and adding a little knot at the side to represent extrude. I thought of replicating the same models and placed them closely together to represent the word pack.
I like this module more than the previous, as it creates a more interesting composition when being placed together.
Process:

I tried out both the silicon and the later method to replicate my model. I started with the silicon method and most of my models crack when I was removing the plaster from the cast. Therefore I tried using latex. Latex was able to capture more details.
Final :

For my final ice tray, I place 4 replicas of my module. I like this configuration most, as it best conveys my key words.

Initial Layout
The modules very too spaced out.

Final Configuration 1



Final Configuration 2

Process Images :

I was helping out with the pouring of silicon , hence I do not have images of process. The process of casting the mold requires teamwork, it was fun and interesting. It was a new learning experience.
Final :

