– The Premise –
———-
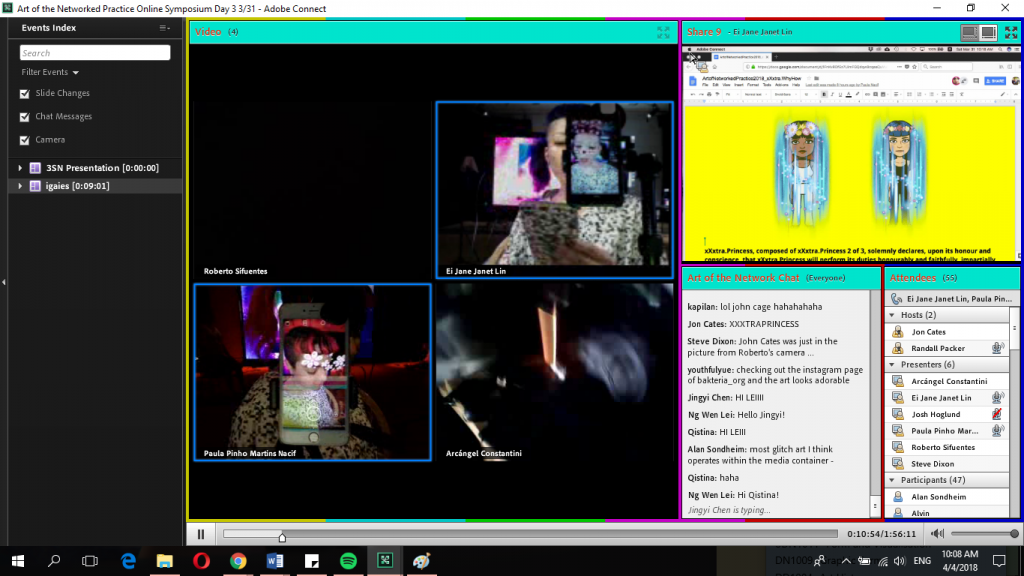
|| Using the social broadcasting platform of Facebook live, my group decided to do an interactive project called ‘Experimental Fashun’ (‘Fashion’ stylised as ‘Fashun’). We split our group of four into pairs whereby one person will be the ‘interviewer’ and the other will the ‘model’. The model’s homework is to select 5 pieces of apparel for a number of sections, namely: tops, bottoms, dresses, accessories and shoes. She will then write down a vague adjective describing the clothing. The ‘interviewer’ will have to engage and collect responses from members of the public from different parts of Singapore to participate in our project. The audience member will have to help the ‘model’ to select pieces of clothing to form their own unique combination. Since the descriptors are rather vague, it mirrors the unpredictable quality of online shopping, whereby we trust frequently vague descriptors and pick from cheap websites like Lazada or Ezbuy. From the selected combinations, we will then photograph proper photos of the whole outfits, pair them in categories of the stereotypes of the different parts of Singapore, and post them on Instagram and add the #experimentalfashun so that users of Instagram can vote for their favourite combinations.
Link to video: https://www.dropbox.com/s/dscw9ljl2ncnhpk/main_FINAL.mp4?dl=0
For this project, our interviewers Bala and Felicia headed down to the following places respectively:
Bala – Sim Lim Square, Bugis Street
Felicia: Bras Basah Shopping Complex, Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts (NAFA), Singapore Management University (SMU) and Lasalle College of the Arts
while Farzana and I were the models camping at home. We waited prepared sets of clothings to show the strangers that were interviewed what they looked like. After the outfits were chosen, we had to take pictures of the full outfit for the Instagram feed.
– Wardrobe Selections –
———-

‘




– The Experience –
———-
During the execution of the Facebook live with Bala, I initially tried to make the clothing in the list as crazy as possible so that the participants would have some pretty crazy descriptors to choose from. However, what we didn’t expect is for them to take the task so seriously! A lot of them were really squinting at the descriptors, trying to clarify and asking for more details so that they could make the most suitable outfit to go for an actual party. This was a lot more significant at Bugis Street where there more more fashionable young people hanging around on a Sunday evening.

Also, we initially intended to put on the outfit immediately after the participant had chosen the outfit, but after we interviewed the first person in Sim Lim Square, we had an awkward moment where the person had to wait for me to change, which probably took about 2 minutes, but there was still a certain social tension that existed even over the Third Space, which was really interesting to observe.

This project was influenced by Blast Theory’s principles of integrating the physical and virtual world together through the use of new technology and inviting audience participation that would influence the outcome of the project, with an element of an immersive narrative. In our project, we set our premise as a fashion showdown modelled after RuPaul’s Drag Race or Project Runway, but incorporating digital elements! Not only did we empower the random participants to be designers themselves, we also involved the Instagram public to pick their favourite outfit to win the fashion show by posting polls

Experimental Fashun was influenced by the concepts of the dynamics of social interaction over the Third Space through social broadcasting, DIWO, and Digital Identity.
Inspired by our Telestroll project, we utilised the medium of Facebook Live to carry out an interview-style social broadcast with members of the public. We explored the concept of DIWO by getting them to make our fashion decisions for us. This links to how we allow others to alter our Digital Identity as well, since clothes are probably the most representative subject of appearance, or how you present yourself to others. Personally, I felt like this project really got me out of my comfort zone as well because I usually do not post a lot of Outfit-of-the-day (OOTD) posts on Instagram or Facebook since I’m not really into fashion myself, and my usual style is super stay-home casual.
By putting on wacky outfits and posting them onto our public Instagram page, I felt like I was allowing my digital image to be altered, and it probably is easier to believe that I’m comfortable putting on weird clothing while I was actually really kind of anxious at the thought of wearing them out in public, especially when we had to shoot the photos of the OOTDs, but I thought that after this experience, I’ve gotten pretty numb to any judgement.
Interestingly enough, we also unintentionally experienced the glitches in human behaviour and technology that we learned would eventually surface when we trapped ourselves in the Third Space for long enough, through the works of Annie Abrahams. The main point is that things would never go the way we intended for them to, for example, with that long awkward waiting time I mentioned above, as well as moments when connection was bad as we moved to different locations so it impaired the communication of the interviewer and model during the Facebook live. In the aspect of human-technology relationships, we also explored the mismatch in expectations in online shopping where you might put your trust in a supplier who you have never bought before, purely based on the pictures and descriptions that they provide, and so the products that you purchase may not end up as what you expected, since you never once inspected the product physically beforehand.

In conclusion, a lot of negotiation was needed to overcome issues, from the conceiving of the idea, to the execution of it, to dealing with unintended glitches. Our outcome for the project also divulged interesting results; we found out that the older demographic preferred brighter colours compared to the younger demographic, and that people in different parts of Singapore had different attitudes towards fashion. We had involved others into our project, be it as a designer who came up with all the wacky combinations, or fashion director who got to say ‘ay’ or ‘nay’ to the outfits, and successfully executed our online fashion project, Experimental Fashun!
- Summarize by stating how your final project explored the idea of the social and how you designed an interactive experience that included both artist and viewers.