Mood Board:








Clothes Reference:










A house for a hermit crab

















To copy the functionality of nature to solve our man-made problems.
Stefanie Nieuwenhuys
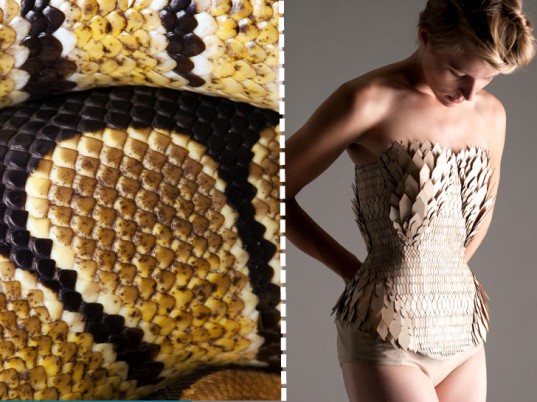




(pictures taken from: https://blogs.3ds.com/fashionlab/stefanie-nieuwenhuyse-recycle-le-bois-comme-des-ecailles-serie-biomimetisme/)
After spying diamond-shaped wood chips on a workshop floor at London’s Kingston University—the leftovers of some architecture student, no doubt—Stefanie Nieuwenhuys was reminded of a secondhand snakeskin bag she once purchased. Scooping them up, the fashion student set to work, layering the wooden scraps onto fabric like reptilian scales.
The artist makes use of scrap material to make her outfits. This project of hers emphasises the idea of reusing materials. Laser cutting the pieces to look like scales, and imitating the layering to look like that of a snake.
Diana Eng

Diana Eng based her “Miura Ori” scarf on an origami “leaf-fold” pattern invented by Koryo Miura, a Japanese space scientist who was in turn inspired by the unfurling mechanism of the hornbeam and beech leaves.
The origami patterns were made by observing nature, and the omission of right angles, like forehead wrinkles or the veins of a dragonfly’s wing. Because of that, the pattern is collapsible.

Monserrat Ciges
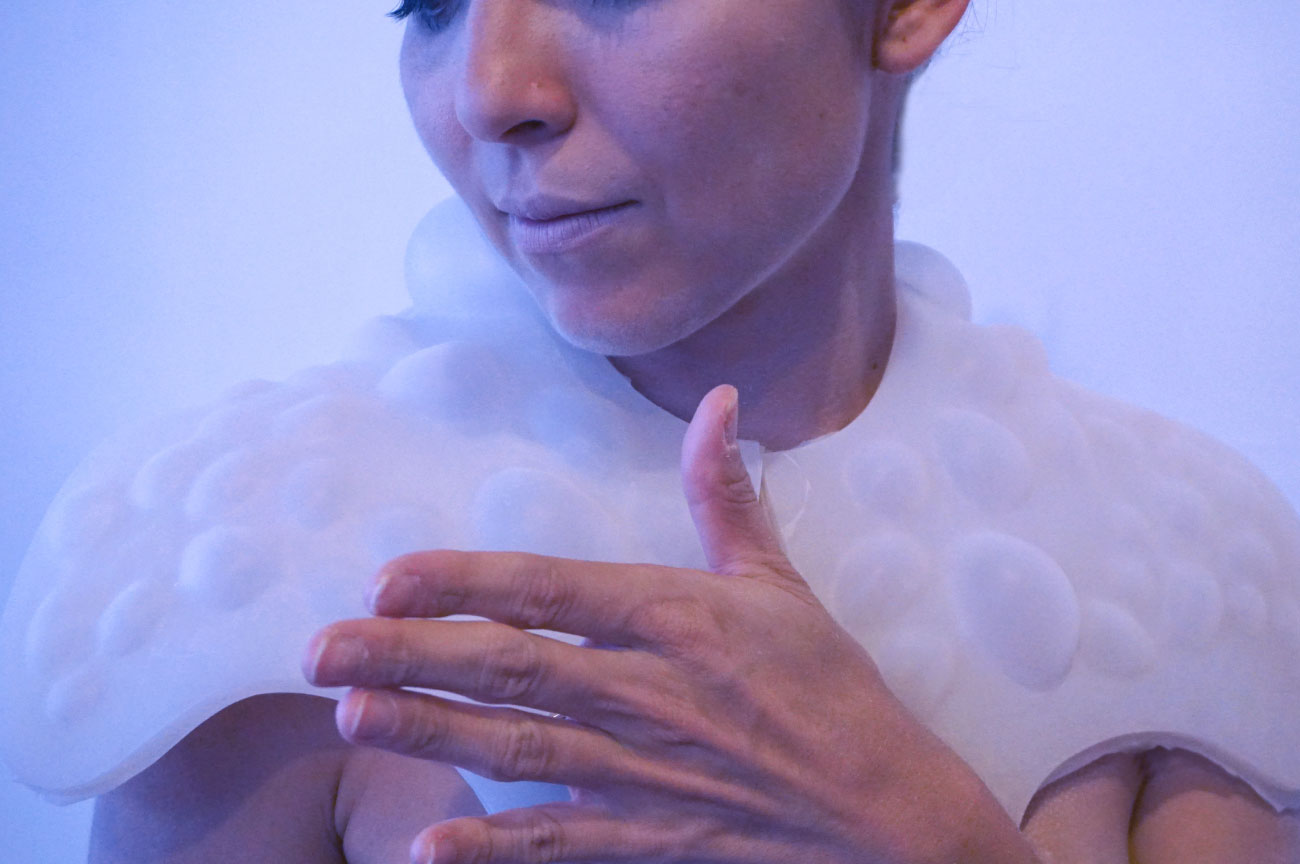
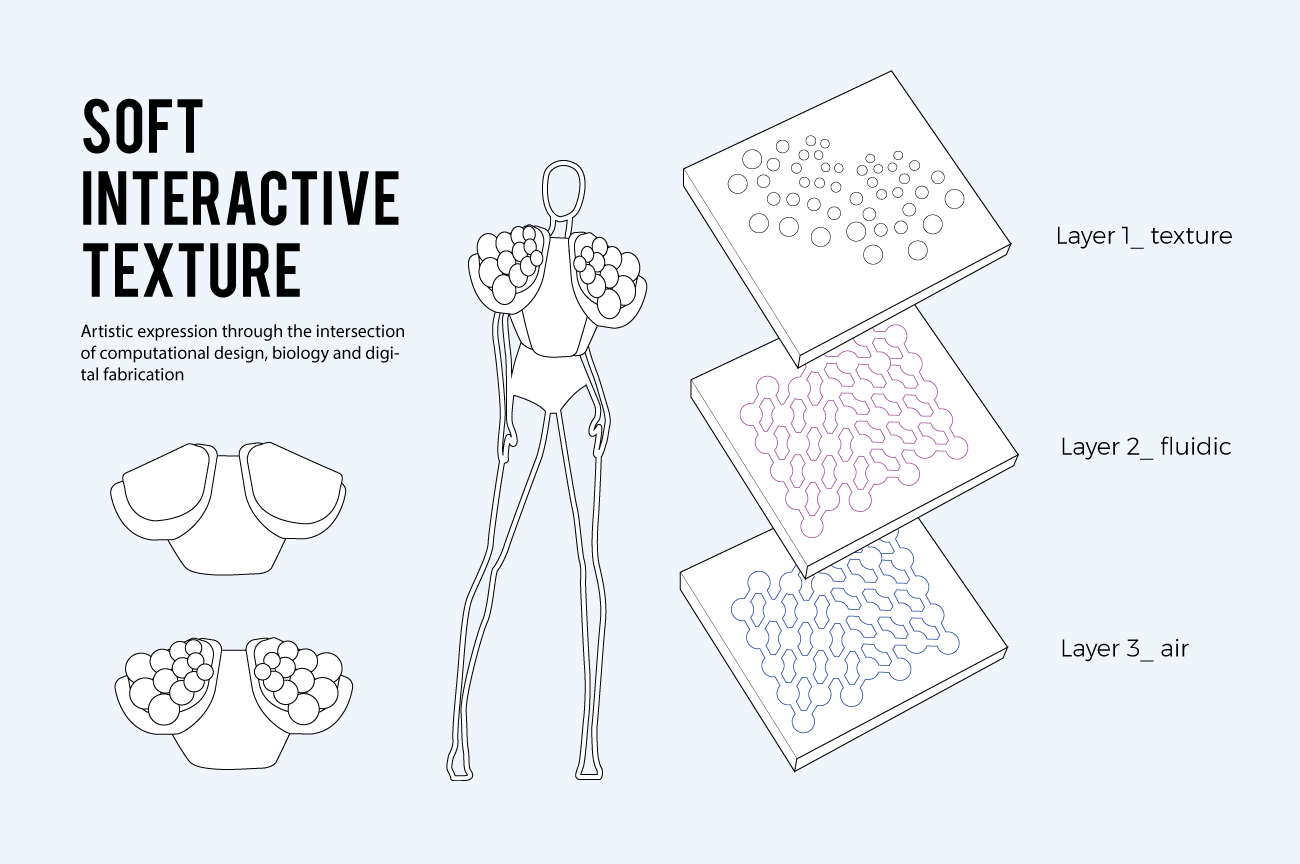

Created to imitate animals that are able to voluntarily self-transform.
References:
Simone Leonelli on the Blurred Boundaries Between Art & Fashion
Fashion Biomimicry Through The Lenses Of Biotechnology, Nanotech And Artificial Intelligence
http://www.osmosis-industries.com/digital/2015/4/21/nature-inspired-fashion-design-through-the-theory-of-biomimicry
Stefanie Nieuwenhuyse Reuses Scrap Wood as Scales – Biomimicry Series
http://www.fairytalefashion.org/
https://class.textile-academy.org/2019/Montserrat/project.html?fbclid=IwAR2HGn6Jnj_R55DxHrH0XUJ-Kps8XhIIsjuXEe7a-0vZX_qN_RzgdFmpEQQ
Designed by Xuedi Chen and Pedro G. C. Oliveira
Photographed By: Roy Rochlin
Model: Heidi Lee
Makeup: Rashad Taylor
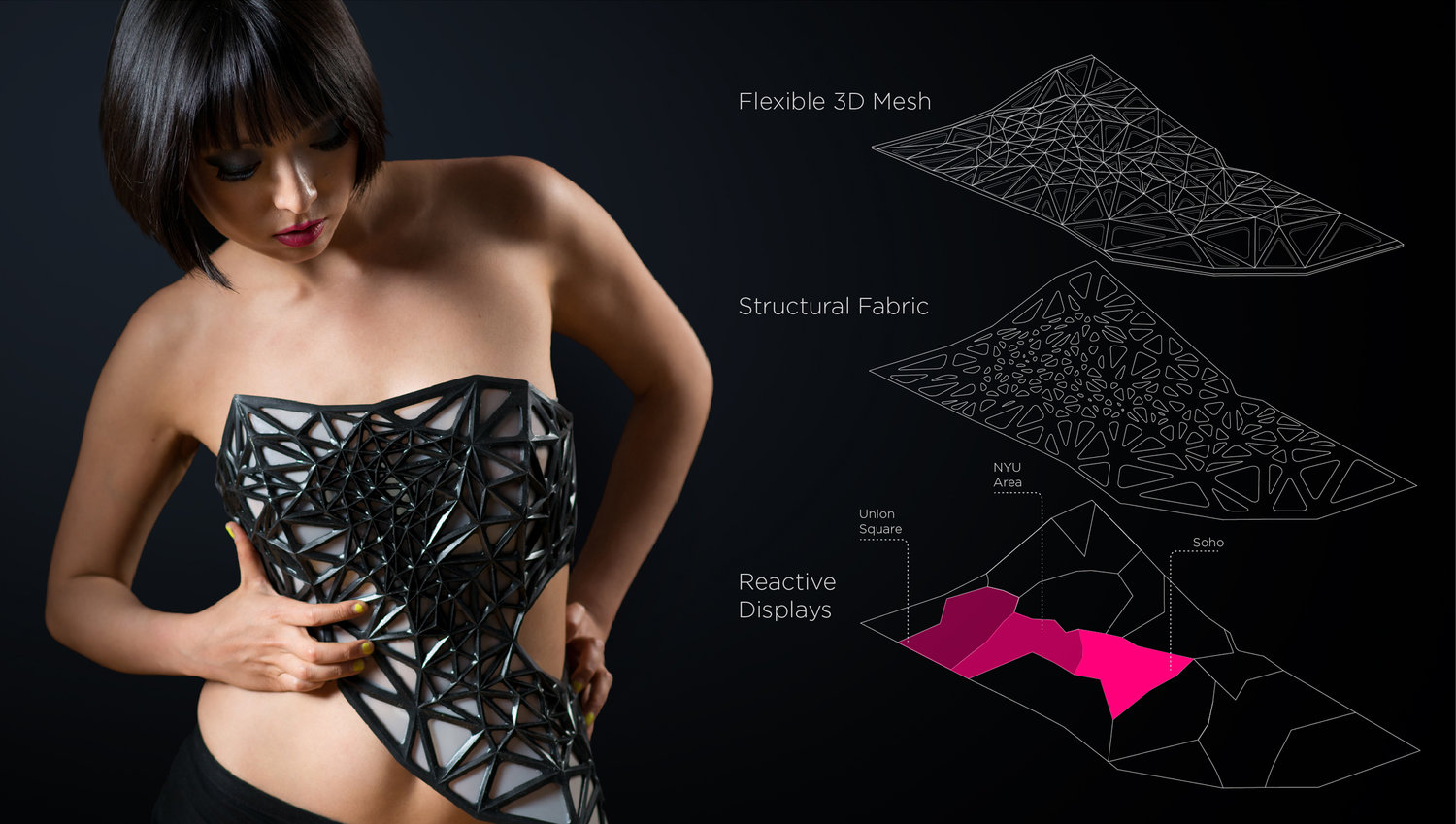
The outfit reflect the amount of data you generate when using the internet. Based on the amount of data generated, it will make parts of the outfit more transparent then the others. It creates a commentary of how transparent one is on the internet despite having things like privacy settings. On Xuedi’s website they states,
By participating in this hyper-connected society while having little to no control of my digital data production, how much of myself do I unknowingly reveal? To what degree does the aggregated metadata collected from me paint an accurate portrait of who I am as a person? What aspects of my individuality are reflected in this portrait?
The work broadcasts the artists’ concern on the wearer, exposing the wearer literally to the public view as contrast to the exposed data we have online.

(photo taken from: https://www.pedro.work/#/xpose/)
According to the artists’ website, the material used for the armature of the outfit is a flexible 3D printed mesh
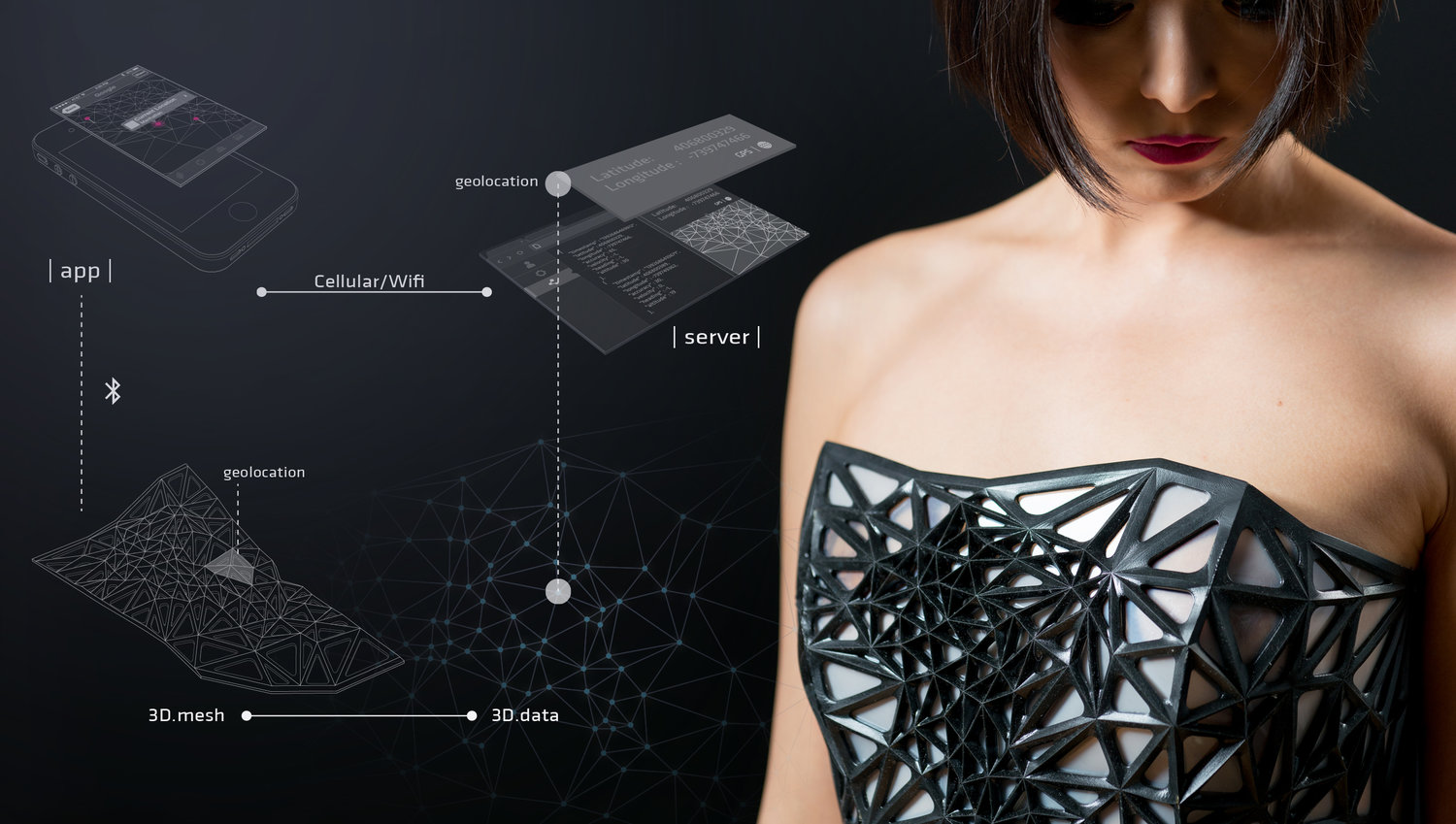
(photo taken from: https://www.pedro.work/#/xpose/)
Subsequently, they also mentioned that the opacity changing material is made from electrochromic film, also the materials used to make smart windows.


(Photos taken from: https://www.explainthatstuff.com/electrochromic-windows.html)
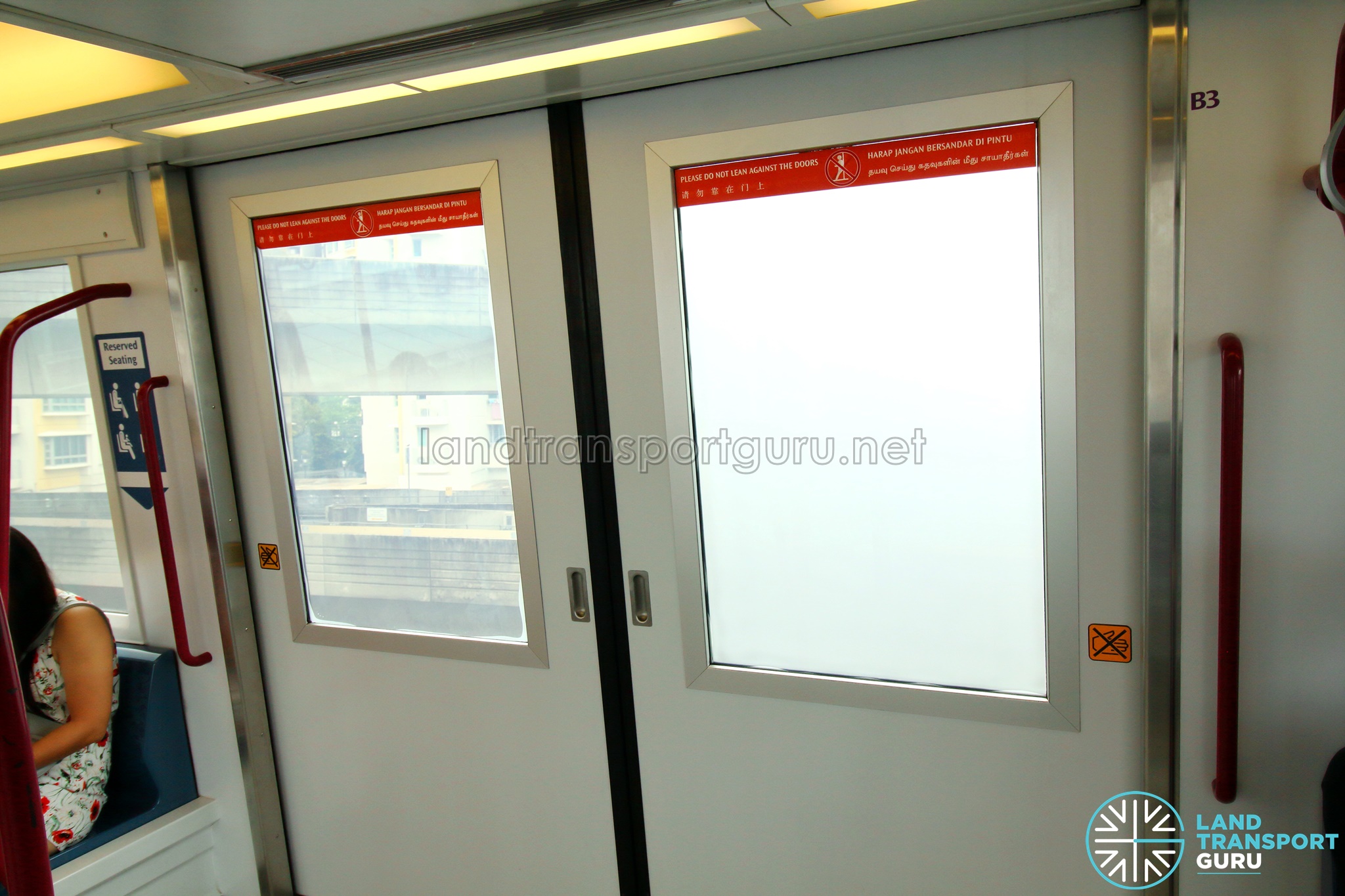

(similar to the material that is used for our LRT windows)
Electrochromic films use technology similar to an LCD display, which uses liquid crystals, under precise electronic control, to change how much light can get through. When the current is switched on, the crystals line up like opening blinds, allowing light to stream straight through; switched off, the crystals orient themselves randomly, scattering any light passing through in random directions, so making the material turn opaque.

(Photo taken from: https://www.explainthatstuff.com/electrochromic-windows.html)